Friday, 24 February 2023
Tuesday, 21 February 2023
SAP LT Replication Server Cockpit - Expert Functions details - Reset Status for Triggers and Logging Tables
Hi Guys,
we frequently use all these functions but must know the details. in this blog, we are going to see about expert functions of SLT Configuration ( SAP)
Note: All this information available in SAP Application
A: Reset Indicator/Status
1: Reset Status for Triggers and Logging Tables
Features
You can use this step to reset flags for the tables listed on the Table Overview tab page.
You can reset the following flags:
•Failed
•In Process
•Logging Table Created
•Trigger State
Selection
You must specify a mass transfer ID. If you want to restrict the selection to certain tables, you can specify in the Table Name fields. Otherwise, the system resets the relevant status for all tables of the mass transfer ID.
You can reset the following flags:
•In Process:
You can reset this flag if a table remains in the status In Process, but does not make any progress. Do not reset this flag if a table is still being processed by a job as some actions could be executed twice for the same table and this could result in errors.
•Failed:
You can reset this flag if a table has the status Failed, and you want to manually reset the flag. This flag can be reset at any time; tables are not processed if they have the status Failed.
•Logging Table Created:
You can reset this flag if you deleted the logging table manually in the source system, and you want to recreate the logging table. For 1:N replication scenarios, you should also ensure that the consumer registration was reset correctly in the source system (you can use the 1:N health check to verify this). If the initial load or the replication is already running for a table, do not recreate missing logging tables as delta tables might already be missing. Instead, you can stop and restart the table in the data provisioning UI (accessible from the Table Overview tab page).
•Trigger State:
You can reset this flag if you deleted the trigger manually in the source system, and you want to recreate the database trigger. If the initial load or the replication is already running for a table, do not recreate the missing triggers as delta tables might already be missing. Instead, you can stop and restart the table in the Data Provisioning dialog box (accessible from the Table Overview tab page).
Thanks
Rupesh Chavan
SLT table replication ABAP dump Error : The current ABAP program "DMC_CALL_OLC" had to be terminated because it found a statement that could not be executed or SYNTAX_ERROR
Applicable to : S4HANA S4CORE 106 S4CORE & SLT SERVER 2.0
Note: due to ABAP dumps if you stopped replication of the respective table still performed the below steps, You would get the message that the table is not available as it's not available in the SLT configuration. Once all steps are executed successfully then add the table again for replication. it will work
Error :
Category ABAP programming error
Runtime Errors SYNTAX_ERROR
ABAP Program /1LT/XXXXX960000100000*****
Application Component Not Assigned
The current ABAP program "DMC_CALL_OLC" had to be terminated because it found a statement that could not be executed.
In include "/1LT/XX96000010000010175TOP", in line 150 of the program
"/1LT/XXXXX96000010000010175", the following syntax errors
Cannot update logging table in the sender system
Error while processing runtime objects
Resolution:
Note: It's recommended to specify the table name in the below Expert Functions to ensure the steps are not run for all tables
1: Choose a configuration in the LTRC transaction on the SLT system and deactivate the configuration.
or open configuration and click on Administration Tab, click on the "Deactivate" button
Go to the "Expert functions" tab
S4HANA Expert functions
SLT SERVER 2.0
1: Double-click on "Reset Runtime Objects Flags"
Note :- in S4HANA 2021 Reset option is not available only the delete the generated runtime modules option is given. please refer above snaps
- Enter in table name, or subset of table names, or leave blank to make changes for all tables
- Click Execute
- Enter in table name, or subset of table names, or leave blank to make changes for all tables
- In function Reset Load and Replication Status, uncheck the first two boxes which are checked when you first see the screen, and check the two boxes which are initially unchecked (see screenshot above)
- Click Execute
4. Go to "Processing Steps" tab
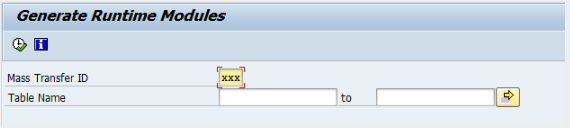
3: Double Click on "Generate Runtime Modules"
- Enter in table name, or subset of table names, or leave blank to make changes for all tables
- Click Execute
- Enter in table name, or subset of table names, or leave blank to make changes for all tables
- "Number of jobs" leave blank
- Click Execute
Now you can add table for replication again.
Thanks
Rupesh Chavan
Wednesday, 15 February 2023
What are different tools use to modifying the SAP software?
SAP provides various tools for modifying the SAP software. Which tools you use depends on the type and extent of your business requirements. Any modifications that you make with these tools are stored in certain tables in the SAP database.
Customizing Tools
The most important configuration tool is the Implementation Guide (). You can use the IMG to make all configurations possible in the SAP standard. Any modifications you make to the SAP software in the IMG are known as Customizing settings, or for short. This includes setting up organizational units (company codes, plants, sales organizations, and so on) and making settings for controlling business processes.
The IMG splits the various Customizing settings into IMG activities and displays them in a hierarchical overview. This overview shows the recommended process flow and assignment to the different applications of the SAP System. The IMG lets you filter out the relevant IMG activities for a particular section of the SAP applications. You can also group IMG activities logically into IMG Projects. These projects are then worked on as an implementation project by a particular team. You can document the requirements of a project and its progress in the IMG Project.
The changes that you make in the IMG are placed in the Customizing tables of the SAP database. The contents of these tables are known as Customizing data. When you use the SAP applications productively, the SAP runtime system analyzes this Customizing data and uses it to control your business processes.
Most Customizing data is client-specific. This means that you can choose different Customizing settings for each client in your SAP System that do not affect each other. Changes to the Customizing settings in one client have no effect on system actions in another client.
However, there is also a significant amount of cross-client Customizing data that is relevant for all clients (such as the factory calendar). These settings are called cross-client Customizing. Note that if you change these types of Customizing settings, it affects all clients in the SAP System.
ABAP Workbench
If the configuration options in the SAP standard are not enough to meet your requirements, you can also add to the SAP standard functions. SAP provides the ABAP Workbench as a complete programming environment. The ABAP Workbench includes tools for defining data structures (ABAP Dictionary), developing ABAP programs (ABAP Editor) and designing interfaces (Screen Painter and Menu Painter), as well as many other functions.
For example, you can use the ABAP Workbench to develop your own report programs or transactions or to modify or make your own enhancements to existing SAP programs. These enhancements are known as customer exits. However, this does require experience of the ABAP Workbench and the SAP application that you want to develop.
The changes that you make in the ABAP Workbench are placed in the Repository tables of the SAP database. The contents of these tables are known as Repository data or Repository objects. Apart from a few exceptions, the Repository data is cross-client. As with cross-client Customizing, changes to Repository objects affect all clients of an SAP System.
Change and Transport System (CTS)
The CTS is the central tool for managing changes to Customizing and Repository data that you make in the IMG or ABAP Workbench. The CTS records all changes in change requests. The changes in change requests can be linked together logically, or can be completely independent of each other. Developers in a team can use a common request. You can create documentation for a change request, where you can describe your changes in more detail. This makes it easier to see which data was changed by which user, and to what purpose.
When you have finished your work in the IMG or ABAP Workbench, or have reached a certain stage, you can release the request. The change request is then used to copy the changes from this client to other clients or systems. This automatic procedure is known as a transport. Transports of changes by the CTS allow you to develop in one environment, test your development work in a test environment, and then, if the tests are successful, use it productively. This makes sure that productive operations are not placed at risk by faulty settings or program errors.
Transports of changes between clients and systems are subject to rules that are set in the CTS configuration in the system landscape. One rule may be that changes are transported into a test environment before they can be copied to the production environment. All transports are logged, so that you can see when a change request was imported into a client or system, and whether there were any errors.
Application Data
In contrast to Customizing and Repository data, application data is not part of the configuration of the SAP software. Application data is the business data that the SAP applications process when you use them productively. It is split up into master data (such as material masters, customer masters and vendor masters) and movement data (such as contracts and financial documents). Application data is always client-specific.
The CTS does not manage changes to application data. It is also impossible to use the CTS to transport application data to other clients or systems.
If you want to copy master data and movement data between clients in an SAP System, or from a non-SAP system into an SAP System, or if you want to set up this data automatically, you can use other tools, such as ALE (Application Link Enabling), CATT (Computer Aided Test Tool), or use the application interfaces of the BOR (Business Object Repository).